114
P a r r I n s t r u m e n t C o m p a n y
One of the modifications
most frequently requested is
a port or other means to feed
liquids, solids, or slurries into
the vessel without removing
the head. This can be done in
various ways.
Ball Valve Solids Charging
Ports
A
ball valve with a 3/8"
diameter opening can
be installed on any one liter
or larger vessel and used
in conjunction with a high
pressure pipette for injecting
slurries under pressure. These
are opened or closed with a
quarter turn of the handle.
Larger diameter valves are
available for 1 gallon and
larger vessels. These ball
valves will withstand the full
pressure developed in a reac-
tor at moderate temperatures,
but their pressure rating falls
off rapidly at temperatures
above 100 °C.
Solids Charging Ports
Part No.
Nominal
Size
Orifice
Diameter,
in.
A143VB
1/4" NPT (F)
0.250
A132VB
3/8" NPT (F)
0.375
396VBAD 1/2" NPT (F) 0.406
Capped Openings
Reactor
Available
Fitting Sizes
Mini
1/4" NPT (F)
1 & 2 Liter
3/8" NPT (F)
Gallon & up 1/2" NPT (F)
Liquid
Complete
Reactor
Mounting
Size, cc
Assembly No.
Thread
Mini
6
A550HC3
1/8" NPT
One Liter
8
A550HC
1/8" NPT
Larger
20
A550HC2
1/8" NPT
A550HC Open
Capped Openings
A
capped opening in the
head of a reactor can
serve as a convenient solids
charging port, offering the
largest possible diameter
and a significantly shorter
passage than a ball valve. A
male connector with a cap
is usually used to close the
opening. These will have a
reliable metal to metal seal
and the ability to withstand the
full temperature and pressure
for which the vessel is rated.
Tubing can be connected
to the fitting, but this type
of connector is normally
used only where solids or
slurries will be added at
atmospheric pressure.
Catalyst Addition Devices
P
arr has developed a unique
device for adding small
amounts of solids (or liquids)
from a sealed container held
within a reactor. It is of particu-
lar interest to users performing
kinetic studies of catalytic
reactions. This device consists
of a small cylindrical chamber
with a cap that is sealed to
the body with an O-ring. It
attaches to the underside of
the vessel head with a 1/8"
NPT connection. To discharge
the contents of the holder, gas
pressure is applied through a
valve installed on the top of
the head. When the applied
pressure is greater than the
pressure within the reac-
tor, the cap is forced open
and the catalyst or other
contents of the holder will
be released into the reac-
tor. This device works best
in the taller, 450 mL and
600 mL Mini Reactors,
and in the 1 liter and
larger Parr Reactors.
A550HC Catalyst
Addition Device
Solids Charging
Auger
A143VB Ball Valve
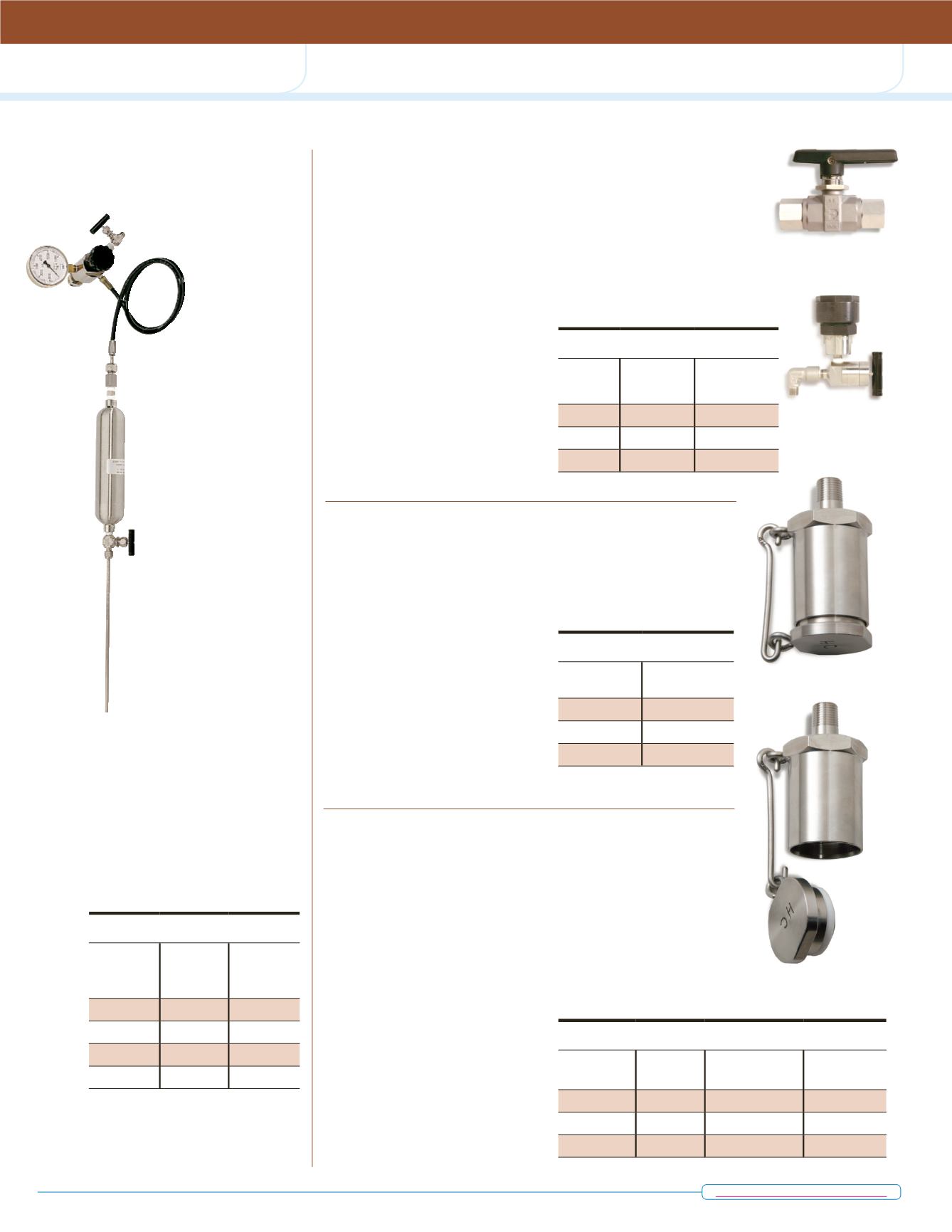
Liquid Charging Pipettes
T
o introduce liquids into
reactors or vessels at
elevated pressures,
the most economical
way is to use
a pressure
pipette as a
secondary
vessel. These
are often used
for liquid addition
to a batch process.
Liquid is forced into the
reactor from the pipette
by applying gas pres-
sure to the pipette
greater than the pres-
sure within the vessel.
If the passages in the
connecting line are
large enough, slurries
or catalyst suspen-
sions can also be
charged into the reac-
tor in this manner.
The pipettes listed
below offer a choice of
volumes and are rated
for pressures to 1800 psi.
They include a nitrogen
filling connection for
attachment to a nitrogen
tank. More elaborate
pipette systems can be
assembled to special order to
include additional fittings, such
as a pressure gage for the
pipette, a pressure relief valve
or a large opening ball valve.
Special pipettes can also be
furnished for higher pressures
to 5000 psi.
A2113HC
Liquid
Charging
Pipette
Liquid Charging Pipettes
Part No.
Pipette
Volume,
mL
Pressure
Rating,
psi
A2113HC3 50
1800
A2113HC4 150
1800
A2113HC 300
1800
A2113HC2 1000
1800
Solids Charging Systems


